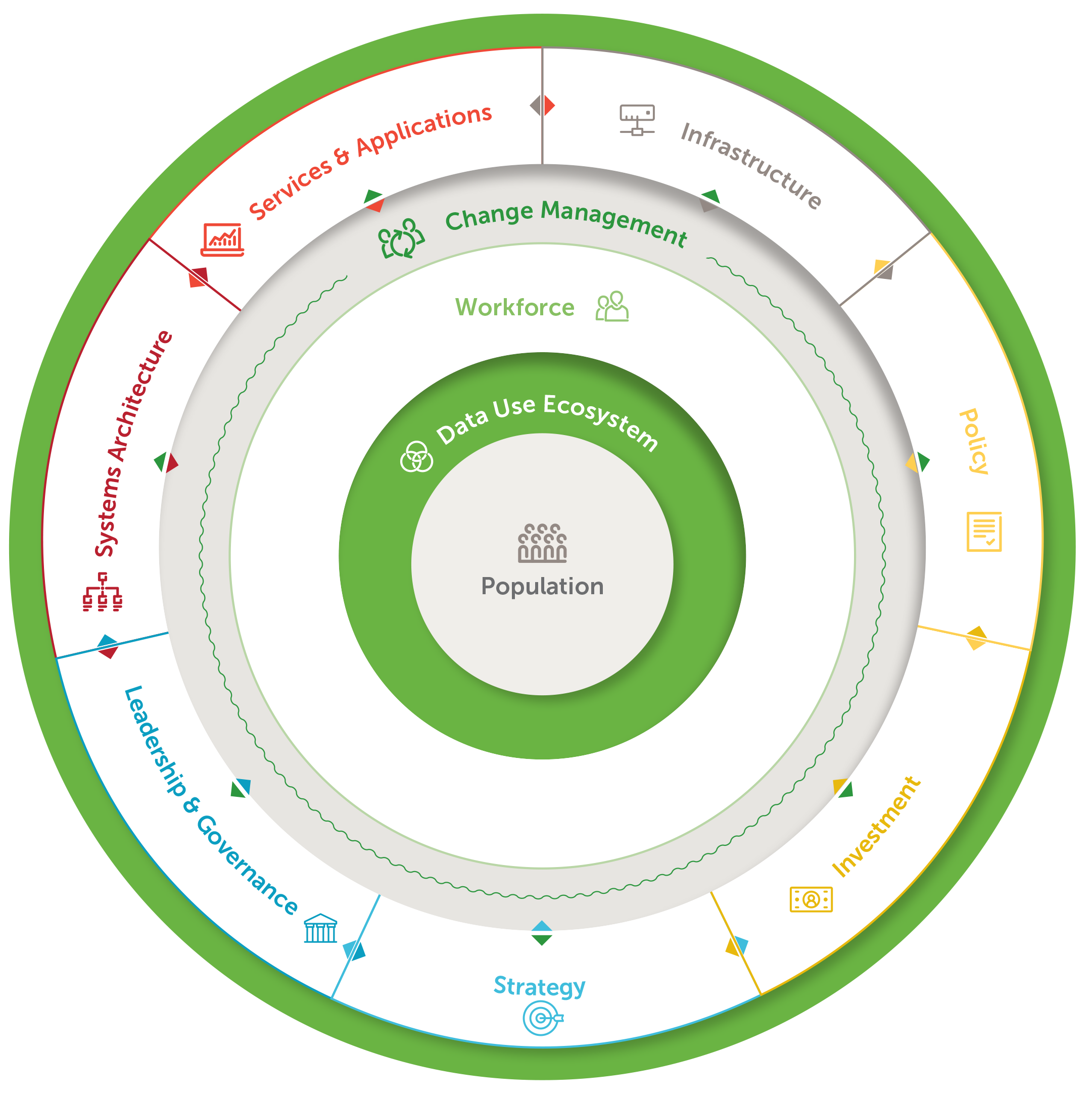
The DUAL model is unique in that it builds on the direct experiences and lessons learned from five countries in Sub-Saharan Africa to identify the essential elements of sustainable digital transformation.
These ten elements go beyond technology and hardware to include the other enabling factors needed to create change—ranging from the development of governance structures to oversee digital initiatives and ensure they meet national standards; to capacity building mechanisms to train the health workforce for its future digital state.
The DUAL model evolves the WHO and ITU Building Blocks to include two new elements of data use ecosystems and change management.
Data use ecosystems encompasses all aspects of data use and access, including data collection, quality, demand, and analysis. This element comprises the patchwork of hardware and software needed to collect, store, analyze, and act upon multiple data sources within a country’s health system.
Change management acknowledges the foundational importance of developing a culture of using data for evidence-based decision-making. It also includes strategies for introducing technology systems to the health workforce to transition to the new tools and ensure widespread adoption.
Without an eye toward the data environment and a purposeful promotion of a culture of data use, digital transformation would not be sustainable. Used together, these ten core elements can support countries with health systems at any stage in their digital transformation journey.